How does multiple testing correction work? 논문 중
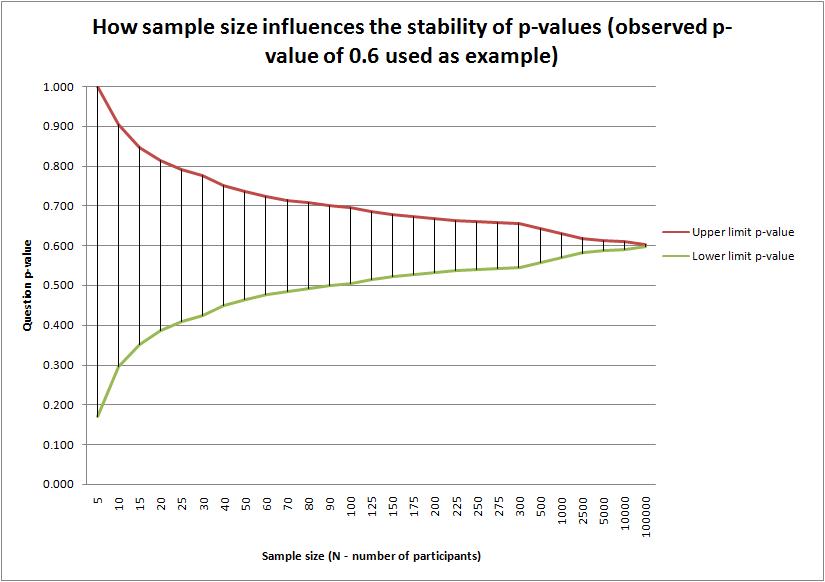
표본 크기가 커지면 표본 오차가 작아지고, 결과적으로 p-value가 작아질 가능성이 높다
(실험수가 높을때 발생할수있는 p-value 오류)
Why P -values are problematic in a high-throughput experiment
Unfortunately, in the context of an experiment that produces many scores, such as scanning a chromosome for CTCF binding sites, reporting a P-value is inappropriate. This is because the P-value is only statistically valid when a single score is computed. For instance, if a single 20-nt sequence had been tested as a match to the CTCF binding site, rather than scanning all of chromosome 21, the P-value could be used directly as a statistical confidence measure.
In contrast, in the example above, 68 million 20-nt sequences were tested. In the case of a score of 17.0, even though it is associated with a seemingly small P-value of 5.5 × 10−7 (the chance of obtaining such a P-value from null data is less than one in a million), scores of 17.0 or larger were in fact observed in a scan of the shuffled genome, owing to the large number of tests performed. We therefore need a 'multiple testing correction' procedure to adjust our statistical confidence measures based on the number of tests performed.
출처 : www.nature.com/articles/nbt1209-1135
출처 : www.questionmark.com/psychometrics-101-sample-size-and-question-difficulty-p-values/
Psychometrics 101: Sample size and question difficulty (p-values) | Questionmark
Posted by Greg Pope With just a week to go before the Questionmark Users Conference, here’s a little taste of the presentation I will be doing on psychometrics. I will also be running a session on Item Analysis and Test Analysis. So, let’s talk about s
www.questionmark.com
'AI월드 > ⚙️AI BOOTCAMP_Section 1' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Confidence interval & CLT_Day8 (0) | 2021.01.07 |
|---|---|
| P-value & Q-value (0) | 2021.01.06 |
| Hypothesis Test, T-test, type of error, parametric_2_Day7(2) (0) | 2021.01.06 |
| Hypothesis Test,자유도,one tail,two tail,chi square _2_Day7 (0) | 2021.01.06 |
| Data Slice , loc , iloc (0) | 2021.01.05 |




댓글